Bacteria Cell Vector Art, Icons, and Graphics for Free Download
Bacterial cell have simpler internal structure. It lacks all membrane bound cell organelles such as mitochondria, lysosome, golgi, endoplasmic reticulum, chloroplast, peroxisome, glyoxysome, and true vacuole. Bacteria also lacks true membrane bound nucleus and nucleolus. The bacterial nucleus is known as nucleoid.

Label the Bacterial Cell Key Best Of Mike S Line Biology Mob University Bio 106 Cell
These can rotate or move in a whip-like motion to move the bacterium. Plant and bacterial cell walls provide structure and protection. Only plant cell walls are made from cellulose. The DNA of.
Bacterial Cell Color Diagram of Organelles Inside the Cell Wall for Science and Biology Concepts
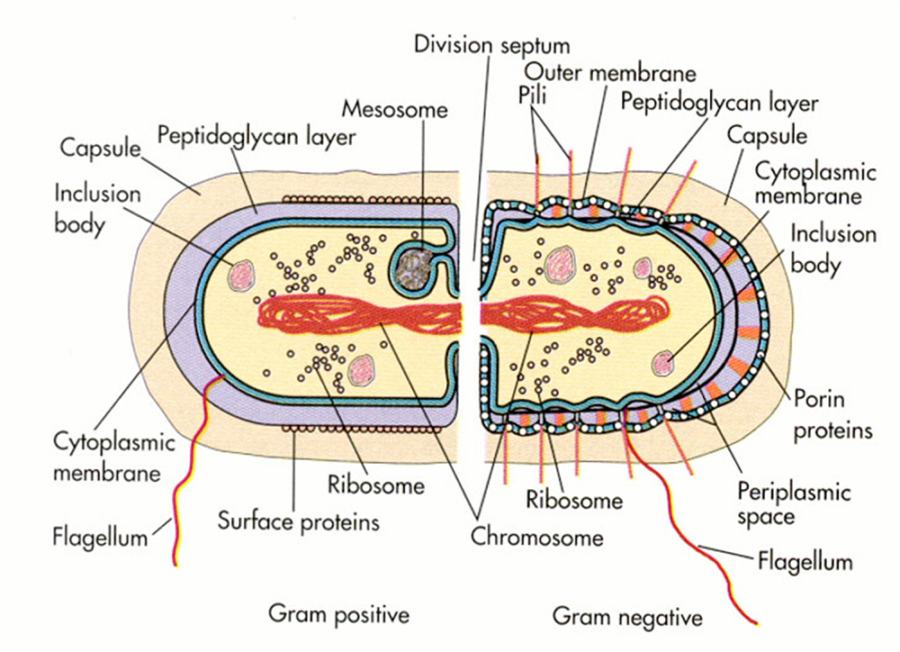
1.11: Prokaryotic Cells. Distinguish between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells in terms of structure, size, and the types of organisms that have these cell types. Identify structures of bacterial cells in models and diagrams, including details of Gram-positive and Gram-negative cell walls and flagella.
Bacterial Cell Diagrams 101 Diagrams
Bacterial cells close bacterial cell A microscopic individual cell of a bacterium. have a more simple structure compared to animal, plant and fungal cells and are usually much smaller.
Bacterial Cell Structure and Function
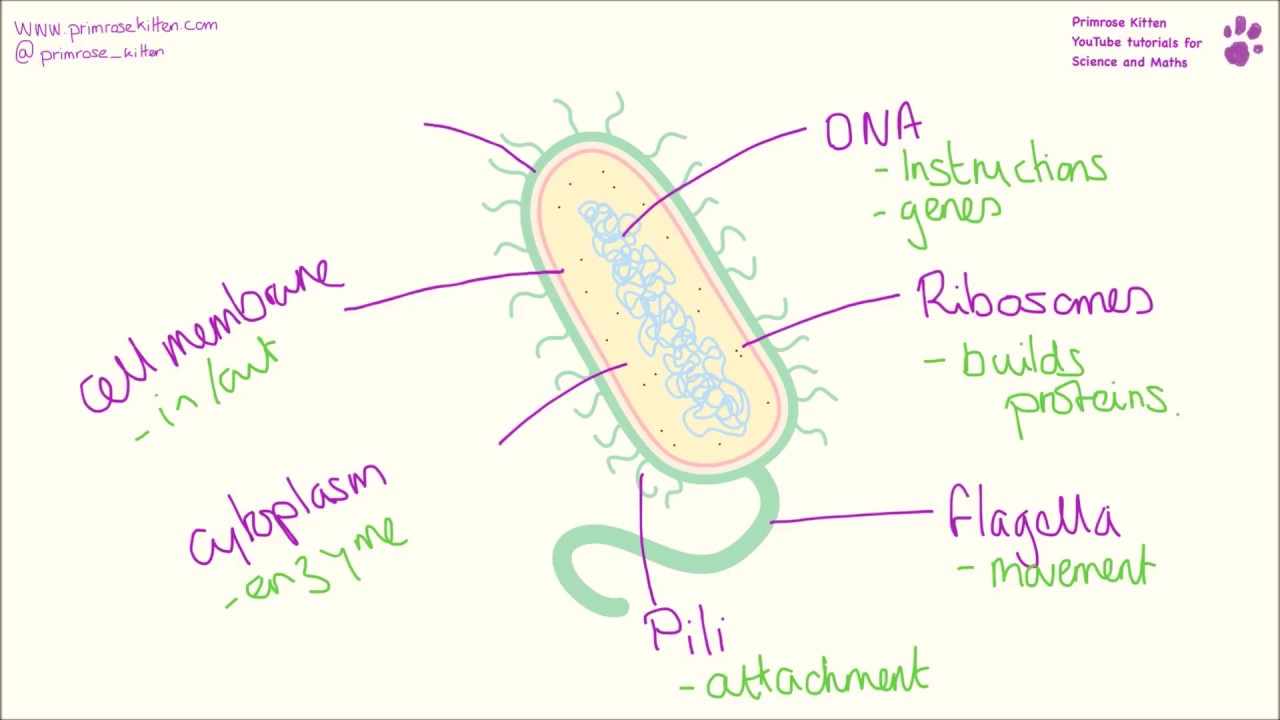
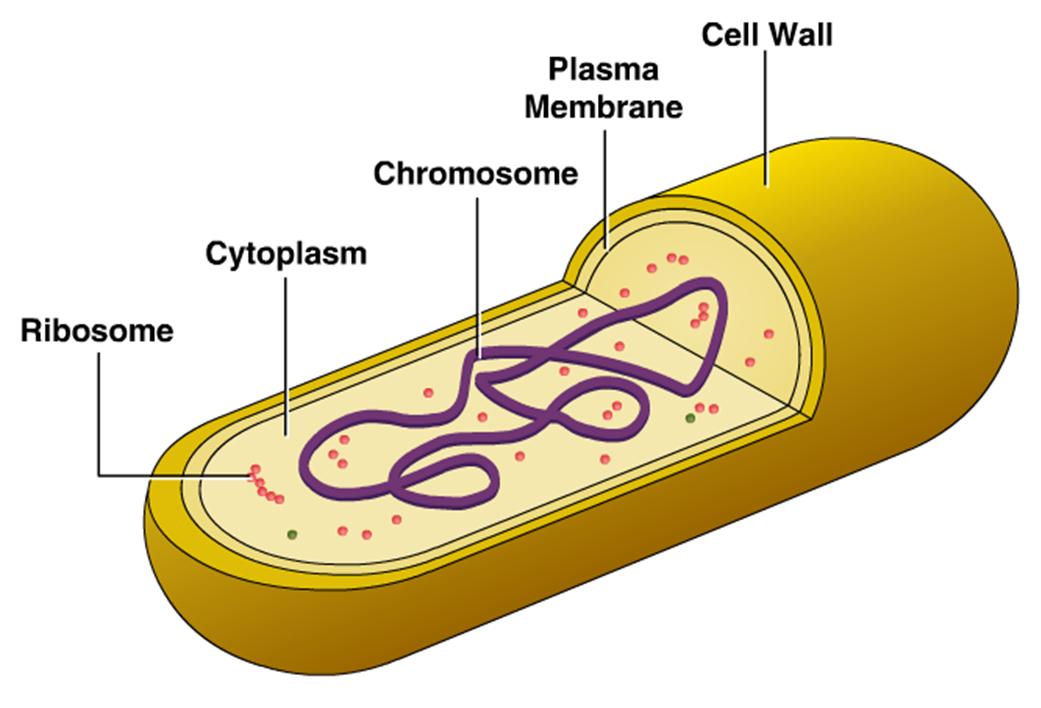
Their structure is a very simple type. Bacteria are prokaryotes because they do not have a well-formed nucleus. A typical bacterial cell is structurally very similar to a plant cell. The cell structure of a bacterial cell consists of a complex membrane and membrane-bound protoplast.

Bacterial Structure Plantlet
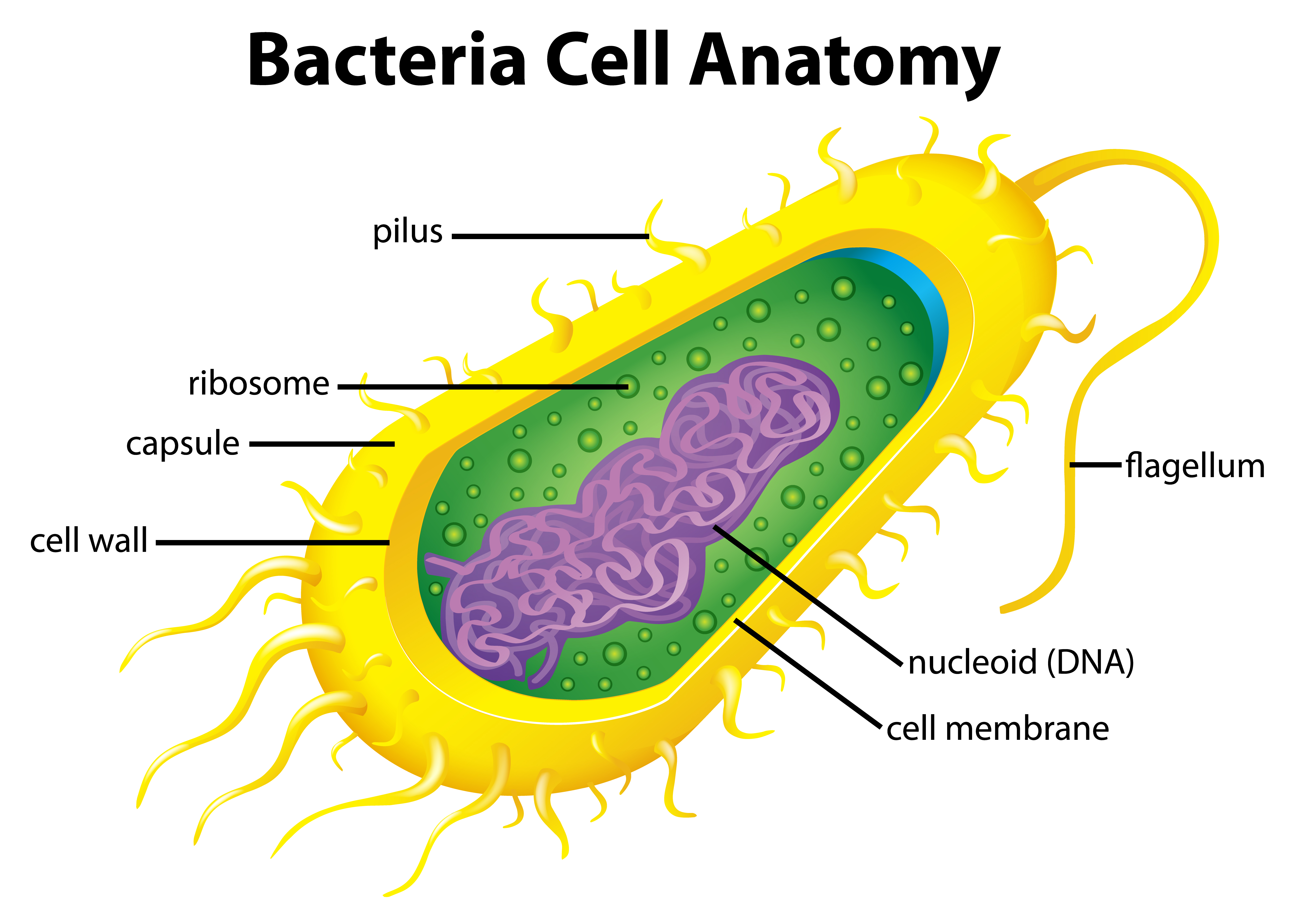
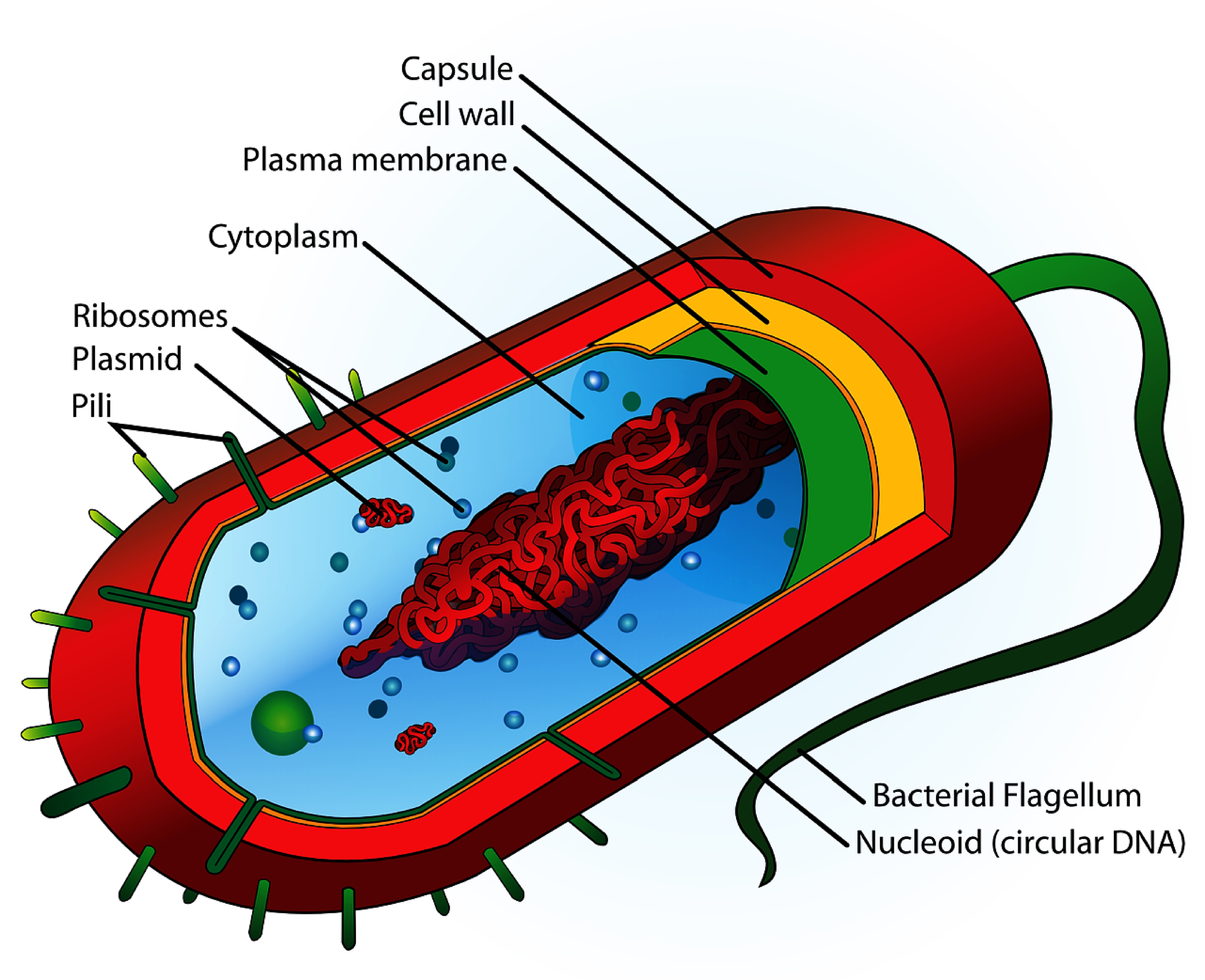
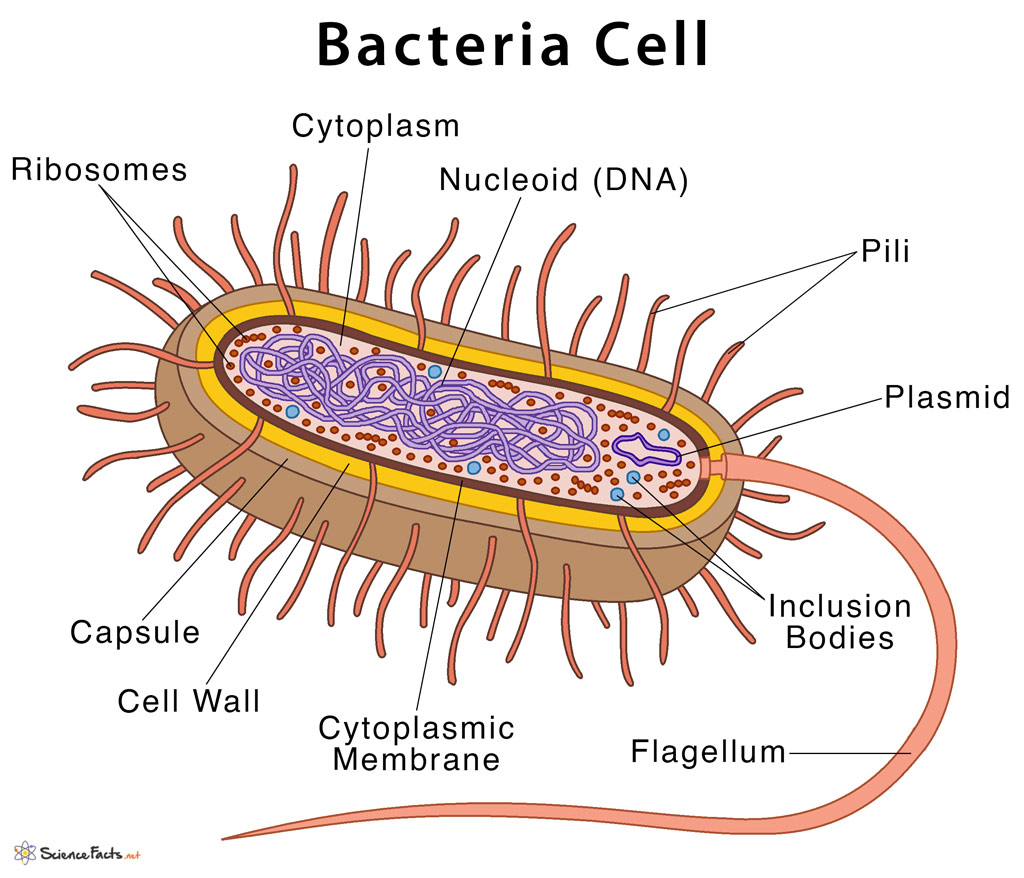
Bacteria Diagram with Labels Bacterial cells have simpler internal structures like Pilus (plural Pili), Cytoplasm, Ribosomes, Capsule, Cell Wall, Plasma membrane, Plasmid, Nucleoid, Flagellum, etc. Labeled Bacteria diagram Eukaryotes have been shown to be more recently evolved than prokaryotic microorganisms.

Bacterial Structure Plantlet
Cell Structure of Bacteria (With Diagram) Article Shared by ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the cell structure of bacteria with the help of diagrams. A bacterial cell (Fig. 2.5) shows a typical prokaryotic structure.
Effective use of alcohol for aromatic blending Tisserand Institute
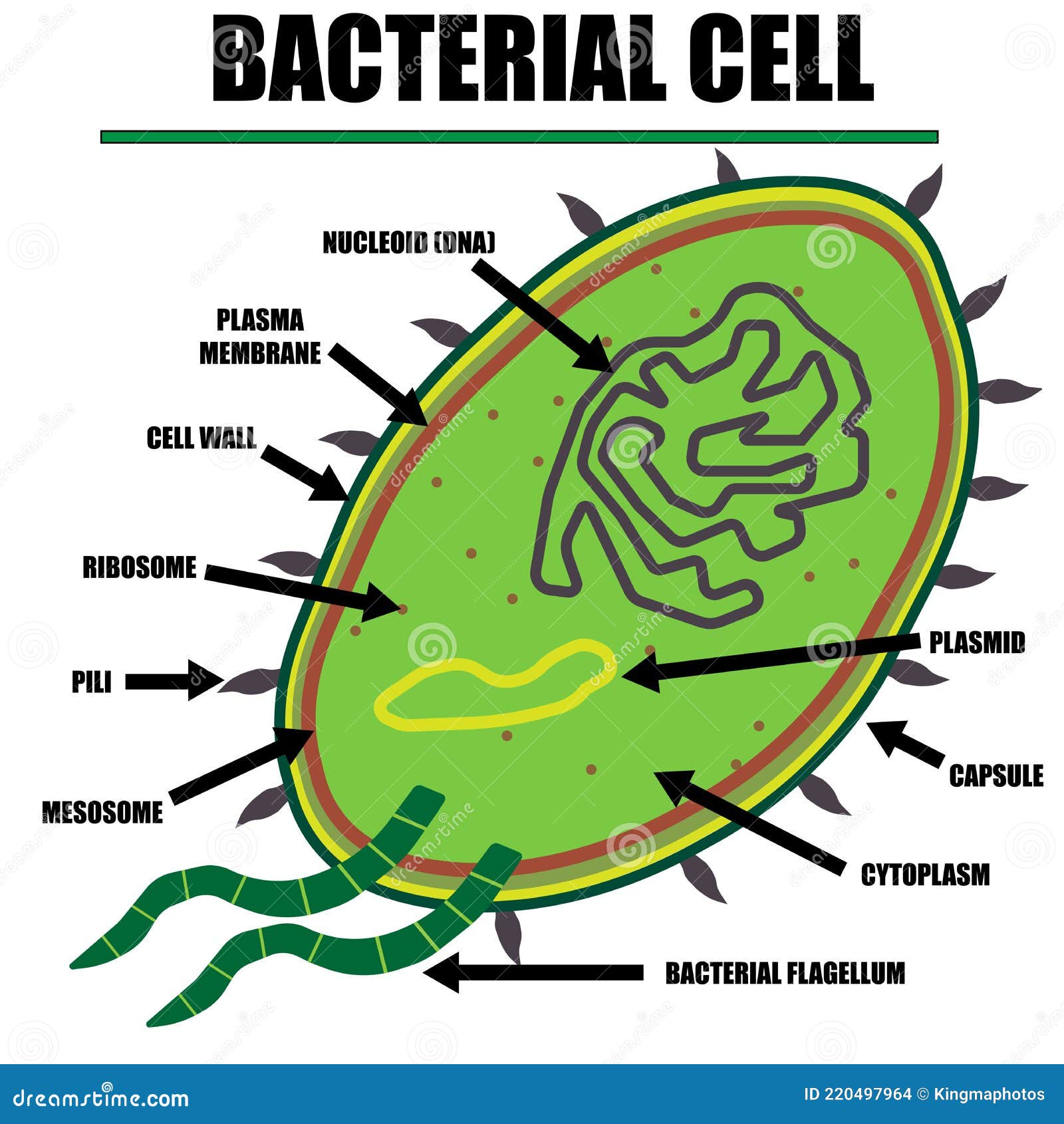
The components are: 1. Cell Envelope 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleoid 4. Plasmids 5. Inclusion Bodies 6. Flagella 7. Pili and Fimbriae. Bacterial Cell: Component # 1. Cell Envelope: It is the outer covering of protoplasm of bacterial cell. Cell envelope consists of 3 components— glycocalyx, cell wall and cell membrane. (i) Glycocalyx (Mucilage Sheath):
Bacterial cell structure and function YouTube
Capsule/Glycocalyx Some bacteria are surrounded by a gelatinous substance which is composed of polysaccharides or polypeptide or both. A thick layer of glycocalyx bound tightly to the cell wall is called capsule. It protects cell from desiccation and antibiotics.
Bacterial Cell Structure and Function
coccus (circle or spherical) bacillus (rod-like) coccobacillus (between a sphere and a rod) spiral (corkscrew-like) filamentous (elongated) Cell shape is generally characteristic of a given bacterial species, but can vary depending on growth conditions.
Bacteria Grade 11 Biology Study Guide
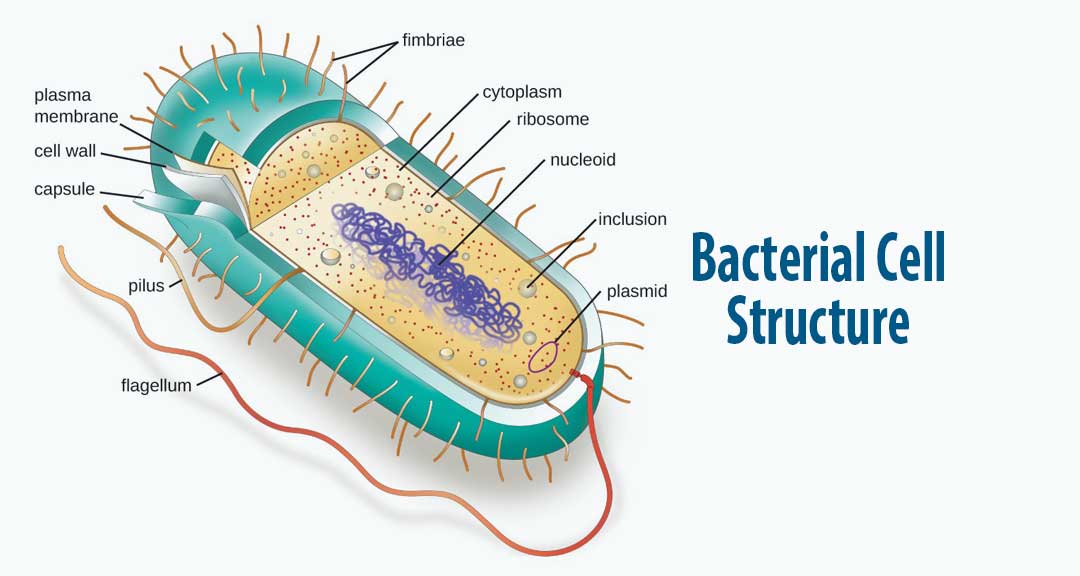
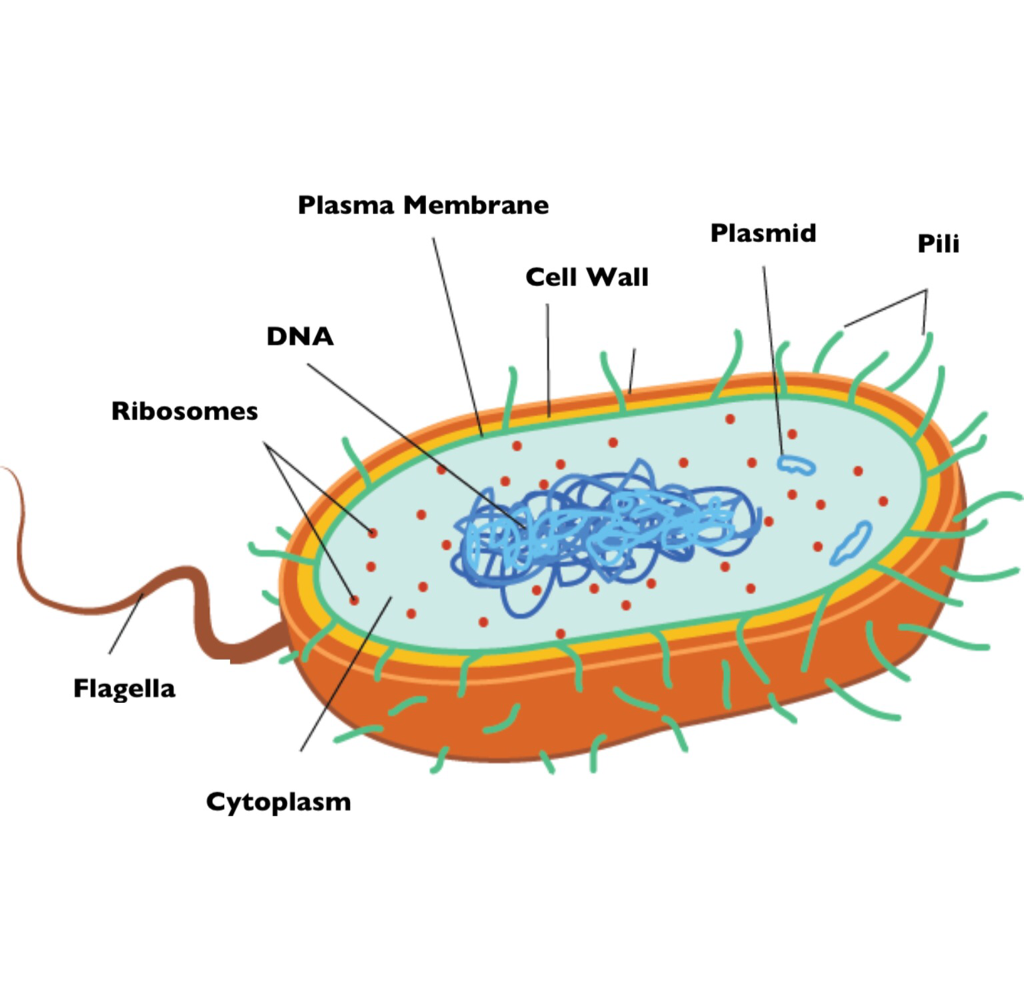
Bacteria Diagram The bacteria diagram given below represents the structure of a typical bacterial cell with its different parts. The cell wall, plasmid, cytoplasm and flagella are clearly marked in the diagram. Bacteria Diagram representing the Structure of Bacteria Ultrastructure of a Bacteria Cell
Characteristics of bacterial cells
The bacteria shapes, structure, and labeled diagrams are discussed below. Table of Contents [ show] Sizes The sizes of bacteria cells that can infect human beings range from 0.1 to 10 micrometers. Some larger types of bacteria such as the rickettsias, mycoplasmas, and chlamydias have similar sizes as the largest types of viruses, the poxviruses.

Bacterial Cell Diagrams 101 Diagrams
In gram-negative bacteria, the cell wall is thin and releases the dye readily when washed with an alcohol or acetone solution. Cytoplasm - The cytoplasm, or protoplasm, of bacterial cells is where the functions for cell growth, metabolism, and replication are carried out. It is a gel-like matrix composed of water, enzymes, nutrients, wastes.

Structure and Function of a Typical Bacterial Cell with Diagram
determined by plane of division determined by separation or not Size - varies Shape and Arrangement-1 Cocci (s., coccus) - spheres diplococci (s., diplococcus) - pairs streptococci - chains staphylococci - grape-like clusters tetrads - 4 cocci in a square sarcinae - cubic configuration of 8 cocci Shape and Arrangement-2

Bacterial Cell Diagrams 101 Diagrams
Bacterial cells were once presumed to be 'bags of enzymes' with minimal oganization 1.Yet, in the past 10 years, numerous studies have demonstrated that bacteria compartmentalize many cellular.
Innovic Medical Bacterial Cell Structure
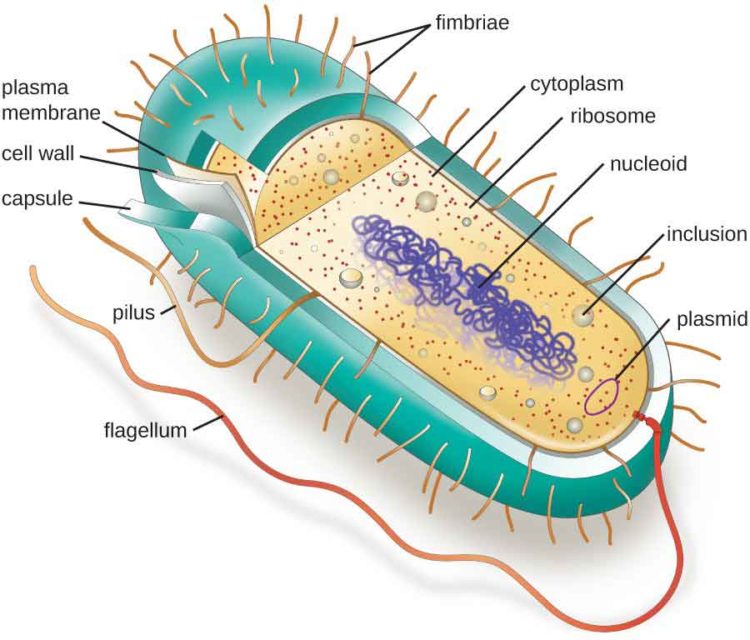
Figure 1. Cutaway drawing of a typical bacterial cell illustrating structural components. See Table 2 below for chemical composition and function of the labeled components. Table 2. Summary of characteristics of typical bacterial cell structures. Structure. Flagella. Function (s) Swimming movement.